Groundwater recharge sources using isotopes and tracers
Abstract
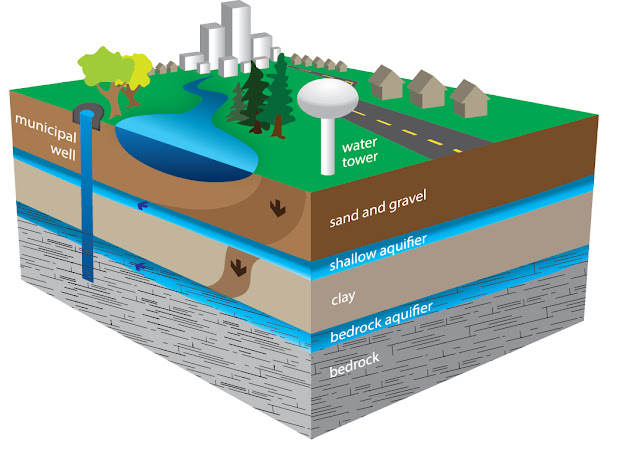
Groundwater recharge sources are local precipitation and surface-water leakage. Isotope exchange along with some evaporation takes place.
Introduction
· Stable isotopes of deuterium and oxygen-18 are natural tracers of water, which are supplied by precipitation.
Groundwater recharge sources are local precipitation and surface-water leakage. Isotope exchange along with some evaporation takes place.


Comments
Post a Comment
Please provide your feedback.