Types of Aquifers
Zones of Soil
The
earth’s crust is lithosphere consisting of rocky materials such as granite,
sandstone, limestone etc.
Basically
soil profile is divided into 2 zones
·
Zone
of aeration (Suspended Water)
·
Zone
of Saturation (Water under pressure)
Now as
cleared from its name aeration zone would be upper than the saturation zone.
Zone of aeration consists of 3 parts
- Soil
moisture zone
- Intermediate belt/Vadoze zone
- Capillary fringe

Image courtesy: Anonymous
Now these
3 parts are arranged from surface to inner level of the Earth. Soil moisture
is that part that consists of water supplied externally to ground by man (irrigation)
or naturally (floods/rain……etc.).This moisture is available to plants roots for
their growth.
Next
come the intermediate belt more commonly known as vadose zone which consists
of soil and rocks and gravels. So this zone is also consisting of blocked air,
which does not allow the water to saturate this area, leading to the blocking
of air molecules inside the vadose zone. That’s why this zone is known as
aeration zone.
Next
comes the part that consists of water rose from the groundwater know as capillary
fringe. Now the water from this zone is rose and is available for plants up
taking.
Zone of Saturation as the name suggests that this zone is fully saturated with water so it is understood that groundwater is a part of this zone. Above the groundwater level there is capillary fringe (in zone of aeration) resulting in the rising of the water from the groundwater level naturally.
Zone of Saturation as the name suggests that this zone is fully saturated with water so it is understood that groundwater is a part of this zone. Above the groundwater level there is capillary fringe (in zone of aeration) resulting in the rising of the water from the groundwater level naturally.
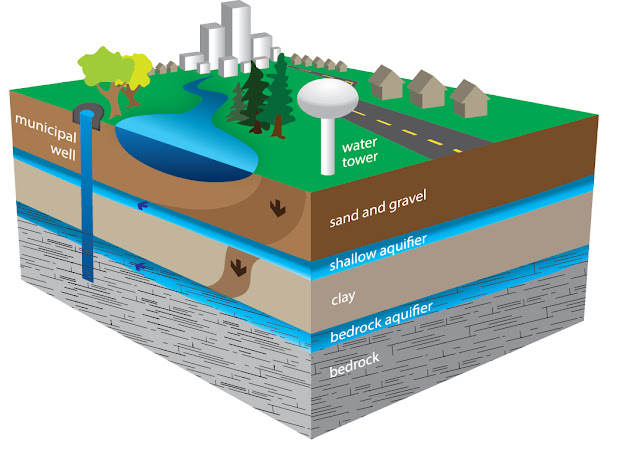
Aquifers or Ground water reservoirs or
water bearing formations
Same
terms used for the extracting groundwater which can be used beneficially due to
its purity (but now even groundwater has begun to pollute main reason involving
the usage of pesticides which enters the surface to meet the groundwater along
with infiltrating water).
Aquifers
types:
- Unconfined/Phreatic
Aquifer
- Confined
Aquifer
- Semi-Confined
Aquifer
- Perched
Well
Unconfined/Phreatic
Aquifer: An unconfined aquifer is permeable bed, only
filled with water lying over a relatively impervious layer. Its boundary is
formed by a free, water table or phreatic level. It is also known as a free,
water table or non-artesian aquifer.
The upper boundary of zone of saturation is known as water table. At water
table the hydrostatic pressure=atmospheric pressure.
Confined
Aquifer: An
aquifer lying between two impermeable layers is said to be confined aquifer. It
is also called artesian aquifer. Because of presence of the upper impermeable
layer the water in this aquifer not being in contact to atmosphere is at a
greater pressure than atmospheric pressure.
Image courtesy: Anonymous
When
a hole I drilled in this aquifer the water rises to a certain level due to the
high pressure, the level to which water rise is known as piezometric level. An
imaginary surface representing the hydrostatic pressure of the confined aquifer
is known as piezometric surface.
The hydrostatic pressure of the aquifer can sufficiently large enough to cause
water to rise up to ground surface level. (As in case of Gurdaspur, Punjab)
Semi-Confined
Aquifer: It is
also known as leaky aquifer. It is formation in which water is present between
2 layers. Upper layer is a semi-pervious layer and bottom one by either
semi-pervious or impervious layer. Semi-pervious layer is a layer that
transmits low yet measurable hydraulic conductivity. In this aquifer the
peizometric and phreatic level are at same level. But after pumping starts, the
piezometric level begins to fall due to vertical uplifting of water. Along with
the fall in piezometric level, there is a fall in the phreatic level also.
·
Semi-Confined
Aquifer with prompt yield:
When phreatic level is lowered almost simultaneously with piezometric level.
·
Semi-Confined
Aquifer with delayed yield:
When there is sufficient time lag between the lowering of the two levels.
Perched Well: A special case of a localised water body in an unconfined aquifer is the
perched water table. It is a water body which has been retarded the downward
flow due to the presence of some earthy materials at some distance above the
water table.
The upper surface of the ground water in such a water body is known as perched
water table.





Comments
Post a Comment
Please provide your feedback.